Introduction
GAP insurance, otherwise known as the Guaranteed Asset Protection is a useful supplement for many drivers, especially for those who are driving financed or leased cars. But how do you tell whether you have this kind of coverage? The problem is that if one has never had to use it, it can quite easily forget that one is or isn’t protected. GAP insurance is needed to be understood if you have it or not because it protects you from a great loss when involved in an accident or if your car is stolen and not recovered. Here, we will show you how to know if you have GAP insurance, how it works, and what to do if you don’t.
What Is GAP Insurance?
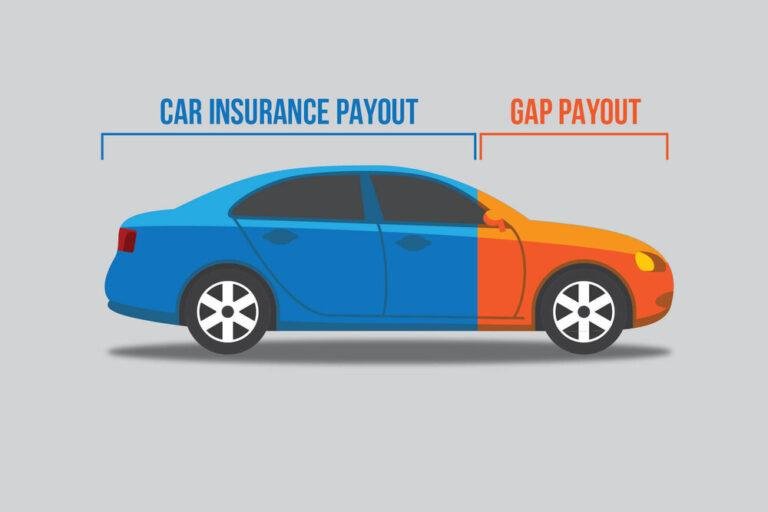
GAP insurance is short for Guaranteed Asset Protection and is insurance against the risk of your car being written off and you owing more than the market value of your car.
For instance, if your car is worth $15000, but you still have to pay $20000 for your loan, then standard auto insurance will only cater for $15000 and this will leave you with $5000, a financial burden you do not want to have. This is where GAP insurance comes to the party pay that amount and guarantee that you don’t need to pay out of your pocket, for that particular amount.
Contrary to normal car insurance where the money is paid for car repairs or for a market price in case your car was a total loss, GAP insurance only pays to close the “gap” between the amount of money you owe on your car loan or lease and the amount that your primary insurance company will pay if your car was written off.
Why Is GAP Insurance Important?
GAP insurance works to your advantage when you have financed or leased an automobile. It is especially helpful in the initial years of car ownership when the car value drops significantly, in most instances, it deteriorates faster than the loan amount repayment process. This means that there will always be a difference between what you are paying and the value of the car.
Here’s why GAP insurance is crucial:
- Rapid Depreciation: New cars lose up to 20% of their value in the first year, leaving a significant difference between their value and your loan amount.
- Total Loss Coverage: If your car is declared a total loss after an accident or is stolen, your insurance company will only cover the actual cash value (ACV) of the vehicle, which might not be enough to pay off your loan.
- Financial Protection: Without GAP insurance, you could end up owing thousands of dollars on a car that you no longer have. GAP insurance ensures that you won’t be left with a large loan to pay off without a car to show for it.
Case Study: For example, if you buy a car with $30,000 and the estimated value of that car in the next year is $22,000. If you wreck the car and you still owe $27,000 on the loan, your main auto insurance will pay only $22,000, which is the value of the car. If you do not have GAP insurance you are actually left to foot the remaining balance of $5,000.
How Do I Check If I Have GAP Insurance?

It can sometimes even require a coin like asking yourself if you happen to have GAP insurance or not when it has been a bit of a question mark if the insurance option was part of your auto loan or not. Below are several methods that you ought to take should you want to discover whether or not you have GAP insurance coverage.
Check Your Car Insurance Policy Documents
The first source of information is official car insurance papers where all the details are supposed to be spelled out on paper. GAP insurance is always optional to the auto insurance plan and may be included in the fine print as an extra fee.
Here’s how to check:
- Locate your policy documents: These might be physical copies, digital files, or accessible via your insurance company’s online portal.
- Look for terms like “GAP coverage” or “Guaranteed Asset Protection”: Check the sections detailing your coverage types and add-ons.
- Contact your insurance provider: If you can’t find specific information in your paperwork, call your insurance company and ask them directly if you have GAP insurance included in your policy.
If you bought GAP insurance on its own, this will not be indicated in your car insurance policy. If so, you’ll have to refer to other documents, like the loan contract or some paperwork received from the dealership.
Contact Your Insurance Provider
If there is still doubt after noting the policy documents they can simply consult the insurance company. Follow these steps:
- Call or email your insurance company: Reach out to their customer service department and ask whether GAP insurance is part of your coverage.
- Prepare key details: Have your policy number and vehicle details handy to speed up the process.
- Ask specific questions: Inquire about the exact terms of your coverage, such as how much GAP insurance covers and whether it applies to total loss situations.
By checking with your provider, you will understand exactly the type of coverage you have, and whether you are covered should you be left with a huge sum that you need to meet in the event of a dreadful mishap.
Review Your Car Loan Agreement
Another prominent example would be where GAP insurance may be added is in your car loan or lease agreement. Some of the lenders particularly those dealing with new cars come with GAP insurance as part of the cost of the deal.
Here’s how to check your loan or lease agreement:
- Find your loan documents: These might be given to you when you signed for the car, or they could be available via your lender’s website.
- Search for GAP-related clauses: Look for a section that mentions GAP insurance or any additional protections included in your loan package.
- Contact your lender: If you’re unsure about any terms, call your lender and ask if GAP insurance was included with your loan or lease.
Sometimes dealerships introduce GAP insurance as an option provided that you take a car on purchase or leasing. If you acquired your car recently, it will be wise to look at the documents you received from the dealership also.
Check With Your Car Dealer

If you bought your car from a dealership then most likely they presented you with GAP insurance at the time of the sale. It is often offered by many dealerships as an addendum to financing incentives or as a feature of financing options.
Here’s what to do:
- Review your purchase paperwork: Find the original documents from when you bought or leased the car. Look for any additional fees or mentions of GAP insurance.
- Call the dealership: Contact the dealership’s finance department and ask if GAP insurance was included in your purchase.
- Ask for a breakdown of charges: Sometimes GAP insurance can be bundled with other services, so it’s important to clarify if it was part of the overall cost.
That way, you’ll be going through these steps to be sure whether you have GAP insurance or not. If you find out you don’t have GAP insurance, the following section will highlight how to determine if you might not have GAP insurance and the next step to take.
What Are the Signs That I Don’t Have GAP Insurance?
Despite people’s belief that they are fully insured, GAP insurance is not always added to standard auto insurance or loan papers as an option. In case you still do not understand, there are a number of indications that indicate you probably do not have GAP insurance.
No Mention of GAP Insurance in Your Policy or Loan Agreement
By far the most obvious sign that you don’t have GAP insurance is failure to find GAP insurance in your insurance policy and the loan you have with the car. If you have scoured your car insurance policy and your car loan agreement and did not see any references made to “GAP insurance,” “Guaranteed Asset Protection,” or similar terms, then chances are, you are not covered.
- What to Look For: Look through sections that detail optional or add-on coverages. If you don’t see anything listed under GAP insurance, you probably don’t have it.
- Next Step: If your review comes up empty, reach out to your insurance provider or lender to confirm that GAP insurance is not included.
Loan Balance Exceeds the Car’s Current Value
The primary purpose of having a GAP insurance is to get the difference between what you still owe your car creditor and the car’s market price in case it is stolen or written off. If you have observed that your loan balance is much higher than your car’s value, and your insurance does not cover this difference; then be assured your car is not protected by GAP insurance.
- Example: If you owe $25,000 on your car but its actual value is $18,000, and there’s no indication of GAP coverage in your documents, you could be responsible for that $7,000 difference in the event of a total loss.
- What to Do: If you’re in this situation, consider purchasing GAP insurance to protect yourself from this financial liability.
Your Insurance Only Covers Market Value
If you have gone through the auto insurance policy documents and realized that your policy only pays the market value of the car in a crash or if it is stolen and declared a total loss then it will come as news to you that GAP insurance is equally not included in your policy. Separate from first-party benefits, standard auto insurance, or, more ordinarily, ‘third party risks’ indemnify in accordance with the car’s devaluation, not the sum you acquired the car at or the money you owe on lease.
- How to Verify: Look for phrases like “actual cash value” in your policy, which refers to the car’s current worth minus depreciation.
- Potential Problem: Without GAP insurance, you might be left paying the difference between the settlement your insurance company provides and what you owe on your vehicle loan.
You Did Not Specifically Request or Purchase GAP Insurance
GAP insurance is generally the type of insurance you have to agree to purchase, with your insurance company, car dealer, or financier. If you cannot remember whether you asked for it the last time you purchased your car or finances the car, chances are, you do not have it.
- What to Consider: If you’re leasing or financing a car, and GAP insurance wasn’t discussed during the purchase process, it’s unlikely to be included by default.
- Action Step: If you realize you didn’t opt for it during the purchase or loan agreement, you can still explore options for adding GAP insurance to your current plan.
Do I Need GAP Insurance?

Still, GAP insurance is not mandatory for every car owner, but it is very useful when you need it. So whether or not you need GAP insurance to as determined by these factors, how you financed your car, the amount you owe on the car loan and the car’s rate of depreciation. Here we will look at who can benefit from GAP insurance and who may not need it and then we will discuss some of the issues that you should bear in mind before you can decide on the right approach.
Who Should Get GAP Insurance?
However, GAP insurance is especially relevant for one category of car owners. You should therefore consider buying GAP insurance if you fall under one or more of the following categories.
- New Car Buyers: If you’ve recently bought a new car, it likely depreciated as soon as you drove it off the lot. New cars lose value quickly, sometimes by as much as 20% in the first year alone. GAP insurance protects you from this rapid depreciation, covering the difference between what you owe and what your car is worth if it’s totaled.
- Financed or Leased Vehicles: If you’re financing or leasing your car, GAP insurance is almost essential. Loans for cars often extend beyond the vehicle’s market value, especially in the early years of repayment. In the case of leased cars, many lease agreements actually require you to carry GAP insurance because the lease terms often leave you owing more than the car’s value in the event of an accident.
- Small Down Payments or Long Loan Terms: If you made a small down payment (less than 20%) or opted for a long loan term (60 months or more), you may owe more than your car is worth for a longer period of time. These conditions increase the likelihood that a “gap” will exist between your loan balance and the car’s value if it’s totaled.
- High-Mileage Drivers: If you put a lot of miles on your car each year, it will depreciate faster than the average vehicle. A high depreciation rate increases the gap between what you owe and what your insurance would pay out after a total loss, making GAP insurance a smart choice for high-mileage drivers.
Who May Not Need GAP Insurance?
It is possible for somebody not to need GAP insurance and it becomes evident that they made the wrong decision. Here are situations where you can likely skip GAP insurance:
- Paid-Off or Close-to-Paid-Off Loans: If you’ve paid off most of your car loan or the remaining balance is less than the vehicle’s market value, you likely don’t need GAP insurance. In this case, your standard auto insurance should cover the remaining balance of your loan in the event of a total loss.
- Large Down Payments: If you made a down payment of 20% or more when you purchased your car, the loan-to-value ratio is probably low enough that GAP insurance isn’t necessary. The lower your loan compared to your car’s value, the smaller the risk of a gap.
- Older Cars with Low Value: GAP insurance is generally designed for newer cars with high loan balances. If your car is older and has already depreciated significantly, the potential gap between what you owe and the car’s value is minimal, meaning GAP insurance might not be worth the cost.
How Much Does GAP Insurance Cost?
The price of GAP insurance depends on the place where you can buy this insurance and its relation to the GAP insurance that is added to your existing coverage or a car loan Currently, GAP insurance costs between $400 and $600 if purchased through the dealership as a part of financing your car or about $20 –$40 annually when acquired as an addition to automobile insurance policy.
Here’s a comparison of GAP insurance costs:
| GAP Insurance Provider | Average Cost | Type of Coverage |
| Car Dealership | $400 – $600 (one-time) | Typically bundled with car loans |
| Auto Insurance Company | $20 – $40 per year | Add-on to existing policy |
| Third-Party Providers | $200 – $400 (one-time) | Separate coverage, outside of loan |
Is GAP Insurance Worth It?
To decide if GAP insurance is worth it, consider the following questions:
- How quickly is your car depreciating?
- How much do you owe on your car loan compared to its market value?
- Can you afford to pay off the loan balance if your car is totaled or stolen?
In most cases, if there’s a significant difference between what you owe and the car’s market value, GAP insurance can save you from a substantial financial burden.
Can You Buy GAP Insurance Separately?

Indeed, GAP insurance may be availed by being bought independently if one did not buy it when they bought their car or if their current auto insurance policy does not include GAP insurance. The GAP insurance can be bought in several ways which include your insurance company, auto dealer, and other insurance companies. Here we shall consider where to purchase GAP insurance as well as how to attach it on a current plan.
Where to Purchase GAP Insurance
If you found out that you never had GAP insurance, you are not totally out of luck because there are ways to get one. Here’s a breakdown of the most common ways to purchase GAP insurance:
- Auto Insurance Companies: Many car insurance companies offer GAP insurance as an add-on to your existing policy. This is typically the most affordable option, with GAP coverage costing an additional $20 to $40 per year on top of your current premium.
- Car Dealerships: Dealerships often sell GAP insurance when you finance a vehicle through them. While convenient, this is usually the most expensive option, with a one-time fee ranging from $400 to $600. Some buyers prefer this option because the cost can be rolled into their monthly car payments, but it’s important to weigh the higher cost.
- Third-Party Providers: There are also independent providers that sell GAP insurance. These third-party companies often offer competitive rates, and you may be able to find a one-time payment plan for $200 to $400. If you prefer not to deal with your dealership or insurance company, this can be a good alternative.
How to Add GAP Insurance to an Existing Policy
If you already enjoy an existing car insurance policy and would like another policy of GAP insurance, the best procedure is generally unproblematic. Here’s what you need to do:
- Contact Your Insurance Provider: Call your current auto insurance provider and ask if they offer GAP insurance as an add-on. Most major insurers provide this option.
- Request a Quote: Your insurance agent will be able to give you a quote for adding GAP coverage to your policy. Make sure you ask about the total cost, as well as any potential impact on your premiums.
- Review the Terms: Before agreeing to the coverage, review the terms of the GAP insurance. Ensure it will cover the full “gap” between your loan and the car’s market value in case of a total loss.
- Update Your Policy: Once you’re satisfied with the terms, your insurer will update your policy to include GAP insurance. It’s important to confirm that the coverage is active and that you have the updated documents for your records.
Is It Too Late to Buy GAP Insurance After the Purchase?
If you didn’t purchase GAP insurance when you initially bought your car, don’t worry you can still add it after the fact. However, there are some important considerations:
- Timing: It’s best to add GAP insurance as soon as possible, especially within the first few years of car ownership when depreciation is highest. The longer you wait, the less beneficial it may be, as your car’s value could start to equal or exceed your loan balance over time.
- Eligibility: Some insurance companies or third-party providers may have restrictions on how old the vehicle can be or how much time has passed since you purchased it. Make sure to inquire about any eligibility requirements when shopping for GAP insurance.
Alternatives to GAP Insurance
If you’re unsure whether GAP insurance is the best option for you, there are a few alternatives that can offer similar protection in case of a total loss or serious accident. Two of the most common alternatives are new car replacement insurance and loan/lease payoff coverage. Each of these alternatives has its own advantages and drawbacks, so it’s important to understand how they differ from GAP insurance.
New Car Replacement Insurance
New car replacement insurance is designed to cover the cost of replacing your car with a brand-new one if your car is totaled within a certain time frame, usually the first one to two years of ownership. Instead of covering the difference between your loan and the car’s value (as GAP insurance does), new car replacement insurance ensures you get a car of similar value to what you originally paid.
How It Works:
- If your car is declared a total loss due to an accident, theft, or natural disaster, new car replacement insurance will pay the full cost to replace the car with a brand-new one, not just the depreciated value.
- This type of insurance is typically available for new cars and must be purchased within a certain period of buying the vehicle (often within one or two years).
Pros:
- Full Replacement Value: Instead of being compensated for your car’s current market value, you get the value of a brand-new car, potentially saving you thousands.
- No Loan Balance Worries: You don’t have to worry about your loan balance versus your car’s value; this policy covers the cost of a new car.
Cons:
- Limited Time Frame: This coverage only applies to new vehicles and is typically available only for a short time (one to two years) after the car is purchased.
- Higher Premiums: New car replacement insurance generally costs more than standard GAP insurance because it covers the full replacement of a new vehicle.
Loan/Lease Payoff Coverage
Loan/lease payoff coverage is another alternative to GAP insurance, and while it works similarly, it usually has more limited coverage. This type of insurance is designed to cover the remaining balance of your loan or lease after your insurance company pays out the actual cash value of your vehicle in the event of a total loss.
How It Works:
- If your car is totaled or stolen, loan/lease payoff coverage will pay the difference between your loan balance and the amount your car insurance covers, up to a certain percentage. This percentage typically caps at around 25% of the car’s value, meaning it may not cover the full gap if you owe significantly more than your car is worth.
Pros:
- More Affordable: Loan/lease payoff coverage is often cheaper than GAP insurance since it offers more limited protection.
- Widely Available: Many insurance companies offer this as an add-on to regular policies, making it easy to obtain.
Cons:
- Partial Coverage: Unlike GAP insurance, which covers the entire difference between your loan and your car’s value, loan/lease payoff coverage may only cover a portion of the gap.
- Lower Cap: The 25% cap may leave you responsible for paying the remainder of your loan out of pocket.
Which Option Is Best for You?
Choosing between GAP insurance, new car replacement insurance, and loan/lease payoff coverage depends on several factors, including:
- Car Age and Loan Amount: If you have a newer car with a high loan balance, GAP insurance or new car replacement insurance might be better options. If your loan balance is relatively small and your car is older, loan/lease payoff coverage might be sufficient.
- Budget: New car replacement insurance tends to be the most expensive option, followed by GAP insurance and loan/lease payoff coverage. Consider how much you’re willing to pay for coverage and the likelihood of needing it.
- Future Plans: If you plan to keep the car for a long time, GAP insurance or loan/lease payoff coverage might be a better choice. If you plan to upgrade to a new car soon, new car replacement insurance could provide peace of mind.
How Long Does GAP Insurance Last?
GAP insurance is not something you need for the entire life of your car loan or lease. It’s specifically designed to cover the period when your loan balance exceeds your car’s market value, which typically occurs in the early years of ownership. In this section, we’ll discuss how long GAP insurance lasts and when it’s safe to cancel it.
When Should You Cancel GAP Insurance?
You can cancel GAP insurance once your loan balance is equal to or less than the market value of your vehicle. This usually happens as your loan payments reduce the balance while your car’s depreciation slows down. At this point, the “gap” between what you owe and what your car is worth no longer exists, making GAP insurance unnecessary.
Signs It’s Time to Cancel:
- Loan Balance is Lower Than Car’s Value: If your loan balance has decreased to a point where it is less than the current value of your car, you don’t need GAP insurance anymore.
- You’ve Made Significant Payments: Large down payments or extra payments made toward the principal of your loan can reduce your loan balance faster. In these cases, you may reach a point where GAP insurance is no longer needed sooner than expected.
- Car Value Has Stabilized: After a few years, the rate of depreciation slows down, and your car’s value levels out. If your car’s value is close to or greater than your loan balance, you can safely drop GAP insurance.
How to Calculate When You No Longer Need GAP Insurance
Determining when it’s safe to cancel GAP insurance involves calculating the current balance of your loan and comparing it to your car’s market value. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Check Your Loan Balance: Contact your lender or log into your loan account to find out your current loan balance. You want to know the exact amount you still owe on the vehicle.
- Determine Your Car’s Current Value: Use tools like Kelley Blue Book, Edmunds, or NADA Guides to estimate your car’s market value. These tools allow you to input details such as your car’s make, model, year, mileage, and condition to get an accurate value.
- Compare the Two: If your loan balance is higher than your car’s market value, GAP insurance is still necessary. However, once your loan balance drops below the car’s value, you can safely cancel the coverage.
Example:
- Let’s say you currently owe $15,000 on your car loan, but your car’s current market value is $17,000. Since the value of your car exceeds the loan balance, you no longer have a gap, and GAP insurance is no longer needed.
How Long Does GAP Insurance Typically Last?
For most people, GAP insurance is only necessary for the first few years of car ownership usually between two to five years depending on the size of the loan, the car’s depreciation rate, and how quickly you pay down the loan.
Here are some general timeframes to consider:
- First 1-2 Years: This is when depreciation is highest, and you are most likely to need GAP insurance, especially if you made a small down payment or have a long-term loan.
- After 3-5 Years: As you pay down your loan and the car’s depreciation slows, the gap between what you owe and the car’s value decreases. At this point, it may be time to reevaluate your need for GAP insurance.
Common Myths About GAP Insurance
There are many myths surrounding GAP insurance that can lead to confusion for car owners. Misunderstanding what GAP insurance covers and when it’s needed can lead to poor financial decisions. Let’s debunk some of the most common myths about GAP insurance to help you make an informed decision.
Myth: GAP Insurance Covers All Types of Damage
Fact: GAP insurance only covers the difference between your car’s current market value and the amount you owe on your loan or lease. It does not cover general repairs, mechanical breakdowns, or damages resulting from accidents that do not lead to a total loss.
Example: If you’re involved in a minor fender bender that results in damage but does not total your car, GAP insurance will not help cover the costs of repairs. Standard car insurance would cover those types of incidents under collision or comprehensive coverage, depending on the cause.
Myth: Everyone Who Finances a Car Needs GAP Insurance
Fact: While GAP insurance is helpful in many cases, it’s not necessary for everyone. As discussed earlier, car owners who make large down payments, have short-term loans, or whose cars are close in value to the loan balance may not need GAP insurance.
Who Doesn’t Need It:
- People who paid a large down payment (20% or more).
- People whose loan balance is close to or less than the car’s market value.
- Owners of cars with low depreciation rates.
Myth: GAP Insurance Is Always Included with Auto Insurance
Fact: GAP insurance is not included in standard auto insurance policies unless specifically added. You must request it as an optional add-on or purchase it separately through your car dealer or a third-party provider. Assuming you have it without checking your policy documents or contacting your insurer can leave you unprotected in the event of a total loss.
What to Do: Review your policy documents or contact your insurer to verify whether you have GAP insurance. If you don’t, you can always add it if you think you need it.
Myth: GAP Insurance Covers Your Car’s Full Purchase Price
Fact: GAP insurance does not cover the original purchase price of your car. Instead, it only covers the difference between what your car is worth at the time of a total loss and the remaining balance of your loan or lease. The purpose of GAP insurance is to help you pay off your loan, not to replace the full value of the car you originally bought.
Example: If you bought a car for $30,000 and it is totaled after a few years, its actual cash value might be $20,000. If you still owe $25,000 on your loan, GAP insurance will cover the $5,000 difference, not the entire $30,000 purchase price.
Myth: GAP Insurance Is Expensive
Fact: While some people think GAP insurance is costly, it’s actually quite affordable, especially if purchased through your auto insurance provider. GAP insurance typically costs around $20 to $40 per year when added to your car insurance policy, making it a relatively low-cost option for financial protection.
Cost Comparison:
- Through your insurance provider: $20–$40 per year.
- Through a dealership: $400–$600 one-time fee.
- Through a third-party provider: $200–$400 one-time fee.
If you’re looking to save on GAP insurance, purchasing it as an add-on to your auto policy is often the most economical choice.
Myth: GAP Insurance Is Only for New Cars
Fact: While GAP insurance is most commonly associated with new cars, it can also be beneficial for used cars that are financed or leased. As long as there is a significant difference between your loan balance and the market value of your vehicle, GAP insurance can protect you from paying out-of-pocket if your car is totaled.
Example: Even if you purchase a used car, if the amount you owe on the loan exceeds its current market value, GAP insurance can help cover the difference.

Conclusion
GAP insurance can be an important safety net for many car owners, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. By understanding what GAP insurance covers, how long you need it, and when to cancel it, you can make sure you’re protected from unexpected financial burdens. Debunking common myths around GAP insurance also ensures you make informed decisions based on accurate information.
If you’re unsure whether you need GAP insurance, start by checking your current coverage, evaluating your loan balance, and comparing it to your vehicle’s value. Ultimately, whether you opt for GAP insurance or one of its alternatives, having the right coverage in place will give you peace of mind.
Follow my blog with Bloglovin